Chat Skill-Based Routing
Chat Platform supports two types of chat routing: manual and automatic routing.
With the default manual routing in place, agents independently pick up customer inquiries from the shared queue. This unassigned queue is shown to agents within their Agent Workspace under the Waiting Response list (each agent's list is refined by filtering out inquiries where visitors have requested agents from different departments or those possessing language skills in other languages).
Automatic routing facilitates the automatic assignment of conversations to agents based on selections made by the Chat Platform service. In this scenario, an agent can also proactively pick up conversations from the shared queue for handling, provided that the preview feature is not disabled.
The Waiting Response section displays only those conversations that have been specifically allocated to a particular agent by the service. This automatic allocation streamlines the workflow for both agents and administrators, while minimizing the likelihood of unattended or delayed responses for visitors.
Types of Automatic Routing
There are two varieties of automatic routing: basic automatic routing and assignment with department prioritization (skill-based routing), which serves as an advanced version of the basic automatic routing.
The skill-based routing allocates chats to agents according to the priorities of departments. Upon enabling this algorithm, the Departments tab appears on the agent editing page, allowing for the prioritization of departments to which the agent is assigned. Primarily, the agent will receive requests from the department with the highest priority (the lowest number)
Using the skill-based routing can solve different problems. For example, it can ensure that a larger proportion of requests from certain departments are handled by specific agents (who are more competent in the direction of the department). However, if the agent is busy, they could take some of the requests from the least "priority" department for themselves, which would allow for a more even distribution of workload among agents and prevent missed requests.
Skill-based routing can also help guarantee that requests from certain departments are addressed first, such as when one department experiences a higher workload than others. Furthermore, skill-based assignment can be activated for departments handling requests from communication channels. The origin of these requests does not impact prioritization, which is determined by the priorities established for the departments.
Description of Chat Routing Modes
In all automatic routing modes, the following agent selection algorithms are possible, depending on the settings of the parameters (all other things being equal):
| auto_assign_priority_ by_last_chat_assigned_ts parameter |
auto_assign_priority_ by_operator_order parameter |
Chat Assignment Scenario |
|---|---|---|
true |
true or false |
To assign a chat among agents with the least number of dialogs (count), the one with the highest number of minutes since the last chat assignment (minimum value of the last_chat_assigned_ts parameter) will be selected. |
false |
true |
To assign a chat among agents with the least number of dialogs (count), the agent with the lowest sorting order value will be selected. |
false |
false |
The chat will be assigned to a random agent among those with the least number of dialogs. |
By default, the auto_assign_priority_by_last_chat_assigned_ts parameter is set to false and the auto_assign_priority_by_operator_order parameter is false.
There are several features available for allocating chats between agents and bots within departments. For information on configuring chat routing between bots and agents, as well as the underlying logic and algorithms for chat distribution, please consult this article.
Basic Chat Routing
Basic Routing takes place first for all online chats, followed by offline chats. Both types of chats proceed through the same algorithm in sequence. Offline chat distribution begins once all online chats have been allocated.
Pass 1: Online Chats
-
The availability of all active agents (those in the Online status) is examined, i.e., the number of open slots each agent has within the
max_chats_per_operatorparameter specified in the account configuration (i.e., how many new chats each can handle given the current number of chats). -
The combinations of departments and communication languages for which each agent is available are determined.
-
For each department and language combination, the list of active agents assigned to the department is sorted in descending order by the number of open slots.
-
Online chats are organized by the time the request was received (i.e., when the chat was created), with older chats being distributed first.
-
The first chat in the sorted list from step 4 is assigned to the chosen agent from step 3.
Pass 2: Offline Chats
Once all online chats have been allocated, offline chats are distributed in a similar manner. The Chat Platform service selects an agent who is in the Online status and:
-
Is authorized to respond to inquiries, i.e., belongs to the appropriate department, see Department registration, and communicates in the language of the request.
-
Has the lowest number of assigned chats, and this number is below the established limit (see below).
If such an agent is identified, the new request is assigned to them. If no such agents are available at the moment, the request remains in the queue awaiting distribution. Agents and administrators can view these requests in the Agent Workspace under the General Queue or Offline Requests list. The administrator can see the length of the undistributed request queue in the Waiting column on the Dashboard.
Skill-Based Routing
Chat Skill-Based Routing initially occurs for all online chats, followed by offline chats. Both chat types proceed through the same algorithm in sequence. Offline chat distribution begins only after all online chats have been allocated.
Pass 1: Online Chats
-
The availability of all active agents (those in the Online status) is analyzed, specifically how many free slots each agent has within the number specified in the
max_chats_per_operatorparameter (i.e., how many new chats each agent can take at the current number of chats). -
For which combinations of departments and communication languages each agent is available and what priority values they have for each combination are calculated.
-
The list of agents with their priorities for different departments and languages is sorted in ascending order of priority levels: from agents with the highest priority for the department of the chat (i.e., the lowest numerical priority value) to agents with the lowest priority.
-
For the element in the sorted priority list from Step 3, queues of chats are taken sequentially in the sorting order corresponding to:
-
the online status of chats (in this case, online chats)
-
the departments and communication languages of the agent for the selected priority
-
-
The minimum chat and queue are selected from those identified in Step 4. The minimum chat in the queue is the first chat within the sorted queue, while the minimum queue is the first queue in the sorted list of queues.
-
The minimum chat from Step 5 is assigned to the agent from Step 2 who has:
-
the highest number of open slots
-
the highest priority for the department to which the chat was received
-
Pass 2: Offline Chats
Once all online chats have been allocated, offline chats are distributed in the same manner.
As a result, during the skill-based assignment of chats from the general queue to agents, it may be observed that earlier-arriving requests are assigned to agents after later-arriving requests. This behavior is accurate and can be explained by the chat distribution logic's nuances. The automatic chat assignment mechanism with department prioritization enabled can be demonstrated through an example.
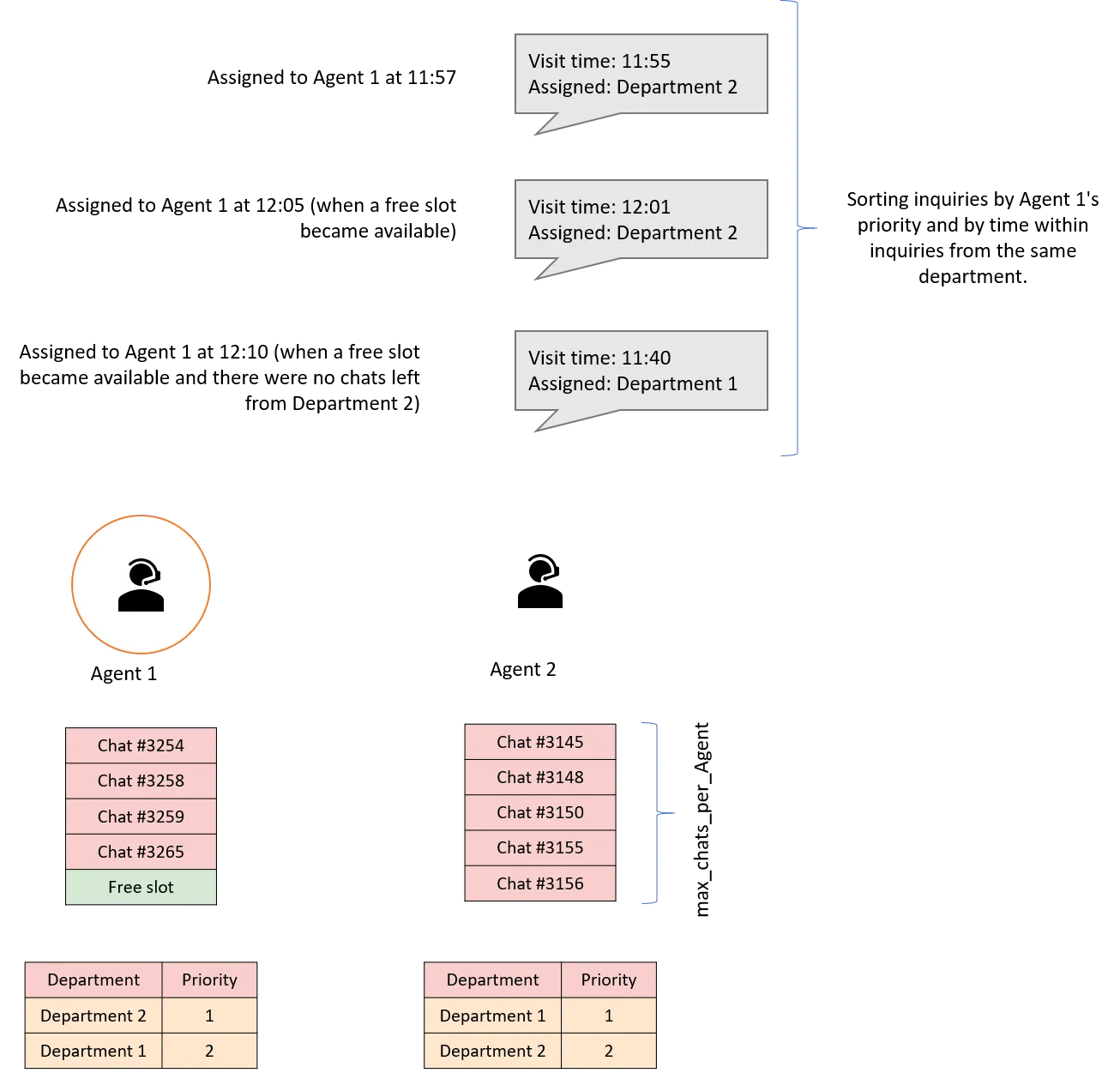
Example
-
Agent 1 has one open slot (i.e., more than Agent 2) and can manage one chat.
-
Chats awaiting auto-assignment are organized according to the agent's priorities (in Agent 1's priority, chats in Department 2 come first, followed by chats in Department 1).
-
Chats for departments are sorted by the time of the request. Among the chats that arrived in Department 2, the chat that arrived at 11:55 has the highest priority (arrived earlier than the other chat in that department). There is only one request in Department 1, and it is queued after the chats in Department 2.
-
The earliest chat from Department 2, which arrived at 11:55, is assigned to the agent.
-
The subsequent request in Department 2, which arrived at 12:01, is assigned to the agent.
-
Since the request in Department 1 was not processed by any other agent during that time (all slots were occupied, or the agent was handling chats from departments with a higher priority), it is assigned to Agent 1 at 12:10 after all the chats in Department 2 were processed. If a new request arrived in Department 2 before this and was not assigned to other agents before Agent 1 became available, it would have had the highest priority and would have been assigned to the agent, causing the request in Department 1 to wait even longer.
As a result, it can be observed that the request submitted earlier (at 11:40) was processed later than the requests submitted at 11:55 and 12:01. This is because the enabled skill-based routing prioritizes assigning requests to the most competent agents for the specific issue.
Administrators can use the analytics features on the Statistics page and track metrics on the Dashboard to evaluate the effectiveness of department priority distribution among different agents. If a pattern emerges where certain departments are assigned unreasonably low priorities (indicated by excessively long chat distribution times in a particular department), it is recommended to review and redistribute department priorities among agents, increasing them for "problematic" departments, or increasing the maximum allowable number of chats for agents.
When skill-based routing is enabled and an administrator adjusts department priorities, the following will occur: upon saving the changes, the settings will be updated (flushed), and the new priorities will take effect during the next 30-second chat assignment cycle. Therefore, the maximum wait time for the settings to take effect is the duration of the settings update operation plus 30 seconds.
Routing of Priority Chats
If the high_priority_urls setting is activated in the account config, chats from priority pages will be distributed first, regardless of the type of auto-routing (with or without skill-based routing) and chat status (online or offline). In this process, the visitor field high_priority will be additionally checked, the value of which is determined by the page from which the visitor initiated the chat. If the field value is equal to 1 (high_priority = "1" - the visitor is on a priority page), this chat will be placed in the queue earlier than others. Then, priority chats (if there are multiple) are sorted by the time of contact.
The high_priority field can also be specified for a visitor(s) independently by the client if it is necessary for chats from certain visitors to be processed first.
Switching between modes
The administrator enables and adjusts the auto-routing function in the General Settings section, on the Additional Features tab:
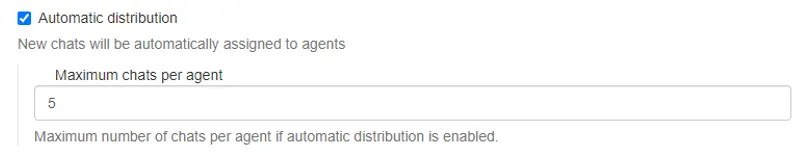
To enable the function:
-
Check the Auto-assignment box.
-
Specify the Maximum number of chats per agent. This value sets a limit, which, when exceeded, will halt auto-assignment for that agent. The default value is 5. Enter the value manually or use the arrows to increase or decrease it.
Additionally, you can configure auto-routing separately for online and offline chats. By default, auto-assignment for offline chats is enabled if auto-assignment for online chats is enabled, and vice versa.
If you want to set a different mode for offline chats, you need to change the auto_assign_offline parameter in the special settings not available through the Control Panel or ask technical support for help.
Department prioritization works in conjunction with enabled auto-routing, which is activated in General Settings (see previous section) and thus sets the true value for the auto_assign parameter.
To enable skill-based routing, you need to set the true value for the operator_department_prioritization parameter (default false). This is done in the account config via a separate URL. If you don't have access to it, contact technical support.
Settings for auto-assignment modes
The following parameters in the account config can be configured for auto-assignment:
| Parameter | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
auto_assign_priority_by_operator_order |
false |
Agent selection during auto-assignment by sorting order rather than randomly. The agent with the minimum order value among the pre-filtered ones is selected. |
auto_assign_priority_by_last_chat_assigned_ts |
true |
Agent selection during auto-assignment based on the time the previous chat was assigned to them. The agent whose last chat was assigned earlier than others among the pre-filtered ones is selected. |
auto_assign_to_last_chat_operator |
true |
The chat is assigned to the agent with whom the visitor had their last chat. |
auto_assign_to_last_chat_operator_if_busy |
false |
The chat is assigned to the agent with whom the visitor had their last chat, regardless of the agent's workload. Only works with auto_assign_to_last_chat_operator = true. |
With skill-based routing enabled, you can additionally set the following settings:
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
default_operator_department_priority |
Integer |
5 |
The default priority value if another value is not set. |
restricted_profiles |
Boolean |
false |
Inability to edit own settings, including department priorities (for agents and supervisors). |
Administrators have the ability to set department priorities for agents and supervisors, while supervisors can adjust the priorities of agents within the departments they oversee, as well as those directly supervised by the supervisor. By default (with the system parameter restricted_profiles = false), both agents and supervisors can modify priority values for their departments. If the parameter restricted_profiles = true, agents and supervisors are not able to edit their own priorities. The default department priority is set to 5.